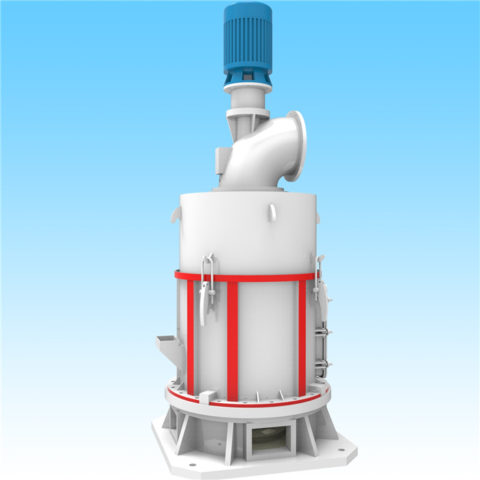
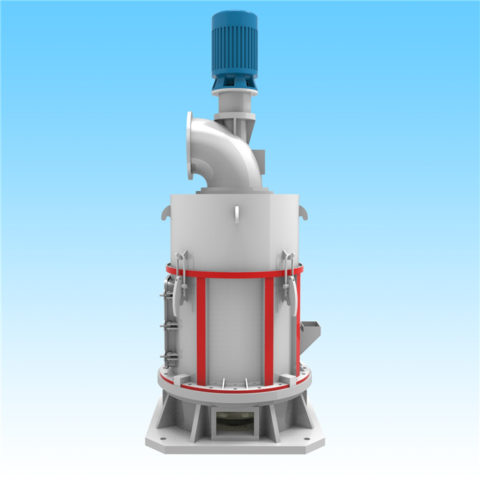
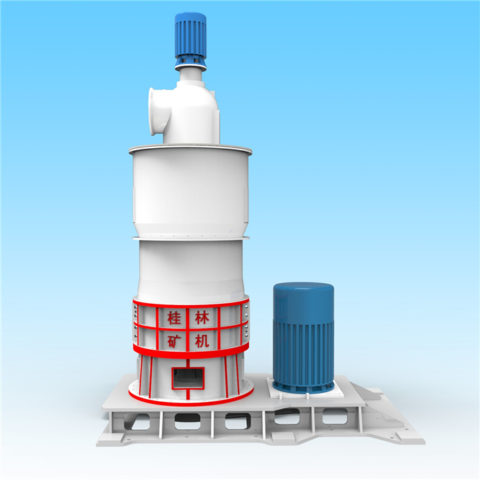
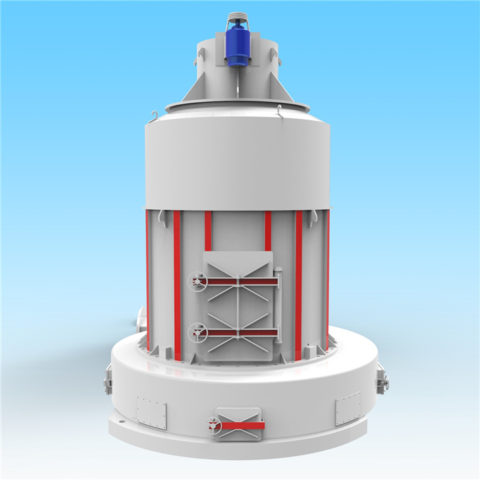
Coal is produced and consumed in many countries, and coal is classified in different ways according to different purposes.
The current classification method is based on the classification of coking coal, which mainly includes: anthracite, lean coal, bituminous coal, lignite, etc. The fixed carbon content in anthracite reaches 93%-98%, and the volatile matter is less than 10%. It is a low-reactivity fuel, and it is difficult to ignite and burn. Lean coal is also called semi-anthracite, and its volatile matter is between 10%-20%. sub-reactive fuel; the volatile content of bituminous coal is generally greater than 14%, and the reactivity is strong, but as the ash content increases, the calorific value decreases and the reactivity is relatively reduced; lignite is a fuel with a low degree of carbonization, with high volatile matter and high It has the characteristics of moisture and low calorific value, and the combustion temperature is relatively low.
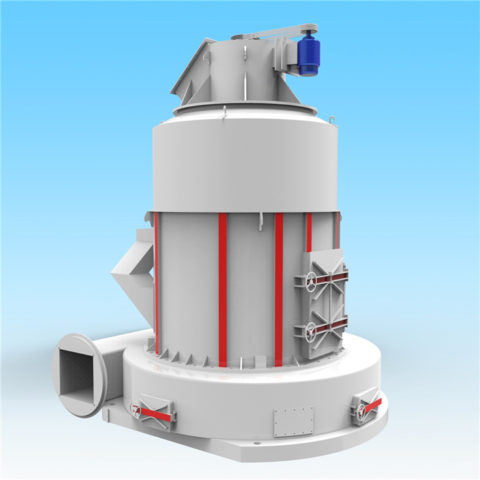
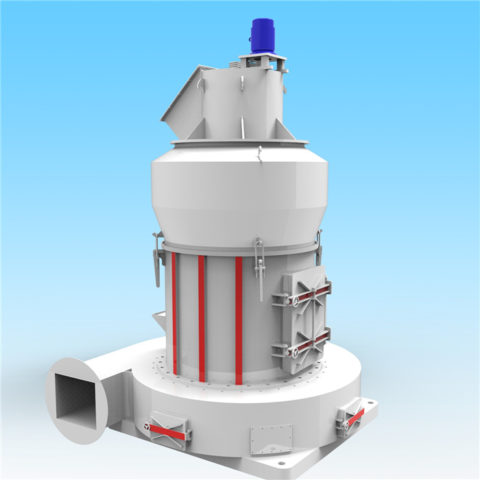
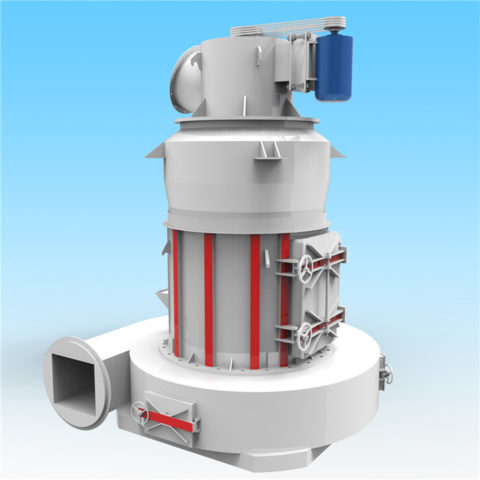
In modern cement industry production, the requirements for pulverized coal quality are closely related to equipment performance, raw material properties, raw meal composition, etc. The main factors affecting pulverized coal combustion are: volatile matter, calorific value, fixed carbon, moisture, sulfur, ash, and fineness.
For the same type of pulverized coal, coarse-particle pulverized coal requires a longer combustion time than fine particles. Therefore, changes in pulverized coal fineness will affect the combustion efficiency and operating conditions of the precalciner kiln system, thereby affecting the performance of the kiln system. heat consumption and production capacity. In the production process of new dry process cement, attention should be paid to the quality and fineness of coal powder to make them reasonably matched to achieve the best economic and social benefits.