A granite powder production line typically involves several stages, including mining, crushing, grinding, and powder processing. Here is a general outline of the process:
Granite is a common type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock that forms from the slow crystallization of magma beneath the Earth’s surface. It is composed mainly of quartz, feldspar, and mica, giving it a granular texture.
Granite powder, which is a byproduct generated during the cutting and grinding of granite stones, has several practical applications across various industries.
1.Mining:
Granite is typically mined from quarries using various methods such as drilling, blasting, or cutting.
The extracted granite blocks are then transported to the processing plant.
2.Crushing:
a. Primary Crushing:
Mined granite blocks, typically obtained from quarries, are transported to the processing plant.
In the primary crushing stage, these blocks are fed into large crushers that break them down into more manageable sizes.
Jaw crushers or gyratory crushers are commonly used for primary crushing.
Jaw crushers are commonly used for primary crushing in granite processing plants.
These crushers consist of a fixed jaw and a moving jaw. The moving jaw is mounted on a pitman that has a reciprocating motion, causing the crushing action.
Granite blocks are fed into the jaw crusher from the top. The size of the feed opening determines the maximum size of the granite fragments that can be fed into the crusher.
The crushed material is discharged at the bottom of the crusher, and it undergoes further size reduction if needed in secondary and tertiary crushing stages.
b. Secondary and Tertiary Crushing:
The partially crushed granite from the primary crushers is further reduced in size through secondary and tertiary crushers.
Cone crushers or impact crushers may be employed in these stages to achieve the desired size reduction.
The objective is to produce uniformly sized fragments suitable for the subsequent grinding process.
Cone Crusher
Operating Principle: Cone crushers operate on the principle of compression crushing. A mantle, mounted on a rotating eccentric, gyrates within a concave bowl. The incoming granite material is crushed between the mantle and the concave.
Advantages:
Cone crushers are versatile and suitable for various types of granite, offering a good reduction ratio.
They produce well-shaped, cubical end products, making them suitable for certain applications, such as in the production of concrete aggregates.
Adjustability: Cone crushers often have adjustable settings, such as the closed-side setting (CSS), allowing operators to control the size of the final product.
Impact crusherImpact Crusher
Operating Principle: Impact crushers, including horizontal shaft impactors and vertical shaft impactors , use the principle of rapid impact to crush granite. In an HSI, material is accelerated by centrifugal force against a high-speed rotor, and in a VSI, material is accelerated against a vertical chamber by the rotor’s centrifugal force.
Advantages:
Impact crushers are suitable for various types of granite and are known for their high reduction ratios.
They can produce a more consistent and cubical-shaped product compared to some cone crushers.
Versatility: Different configurations of impact crushers provide versatility for different applications and end-product specifications.
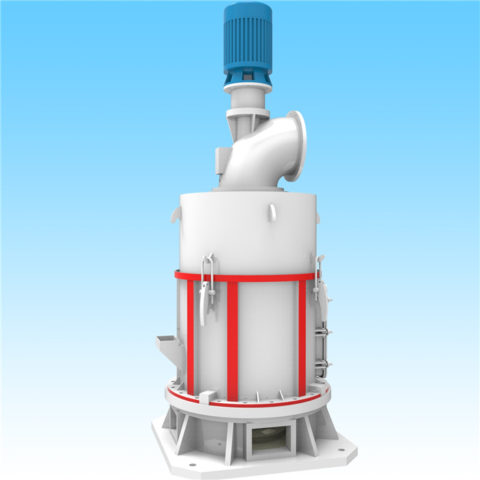
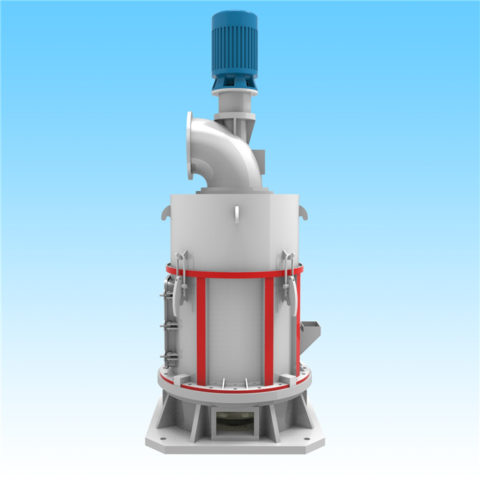
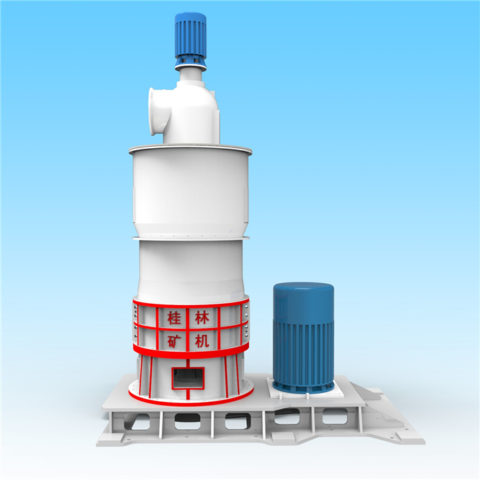
3.Grinding:
a. Grinding Process:
The crushed granite fragments are then subjected to grinding to create granite powder.
Grinding can take place in various types of mills, depending on the specific requirements and the desired particle size distribution.
Ball mills, rod mills, and vertical mills are commonly used in the mining and mineral processing industry for grinding operations.
Operation: Raymond roller mills consist of one or more rollers that rotate around a horizontal axis, crushing and grinding the material between them.
Advantages:
Efficient for grinding a wide range of materials.
Can provide precise control over particle size distribution.
Suitable for both coarse and fine grinding.
b. Particle Size Distribution:
Achieving the desired particle size distribution is crucial in the grinding stage.
Control systems and monitoring devices are employed to ensure that the ground granite powder meets the specified particle size requirements.
The grinding process may involve multiple stages to refine the particle size further.
4.Powder Processing:
a. General Processing:
The ground granite powder undergoes additional processing to meet specific requirements.
Depending on the intended applications, additional steps such as classification, separation, and purification may be incorporated.
b. Technologies Used:
Air classifiers or sieving equipment may be employed to classify particles based on size.
Separation techniques, such as magnetic or gravity separation, might be used to remove impurities or separate different components.
Purification processes may involve washing or chemical treatments to enhance the quality of the final product.
c. Quality Control:
Quality control measures are implemented throughout the powder processing stage to ensure that the product meets industry standards.
Regular testing for particle size distribution, chemical composition, and other relevant properties is carried out.
Adjustments to the processing parameters may be made to maintain product consistency.
5.Packaging and Distribution:
Once the granite powder meets the desired specifications, it is packaged for distribution.
Packaging can be done in bags, bulk containers, or other suitable forms based on customer requirements.
6.Quality Control:
Throughout the production process, quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the granite powder meets industry standards and customer specifications.
This may include regular testing for particle size distribution, chemical composition, and other relevant properties.
7.Environmental Considerations:
It’s essential to consider environmental impact during the production process. This includes managing waste, water usage, and any potential environmental hazards associated with the mining and processing of granite.
8.Safety Measures:
Safety protocols should be in place to ensure the well-being of workers involved in the production process. This includes proper equipment maintenance, use of personal protective equipment, and adherence to safety guidelines.
The specific details of a granite powder production line can vary based on the type of granite, the intended use of the powder, and the scale of the operation. It’s crucial to follow industry standards, regulations, and best practices to ensure efficient and sustainable production.