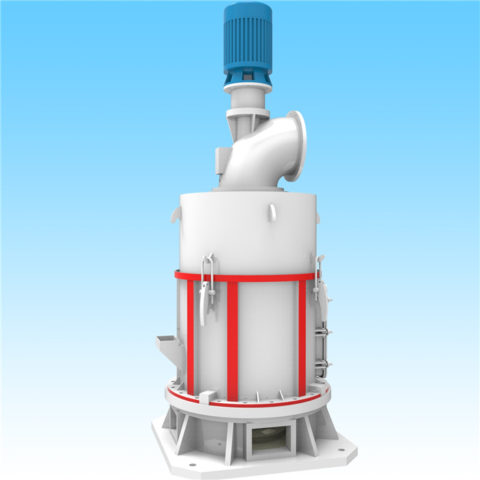
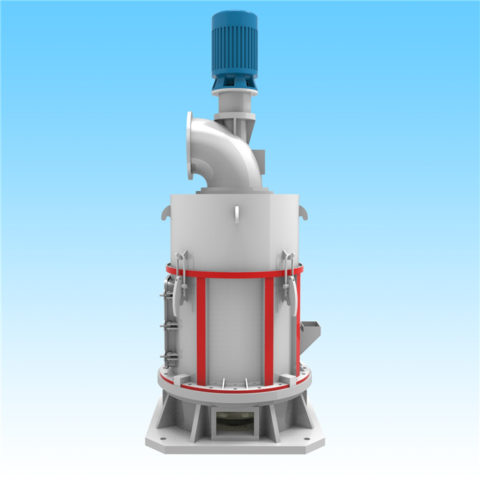
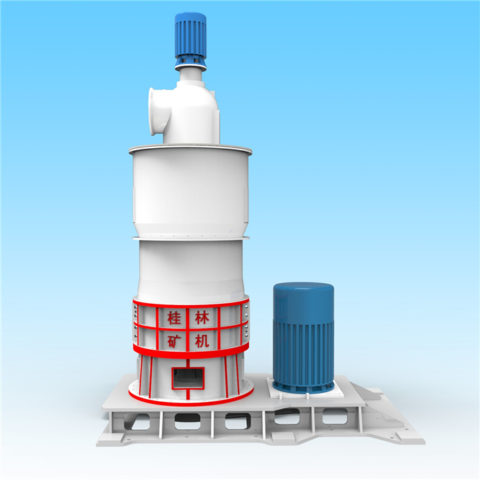
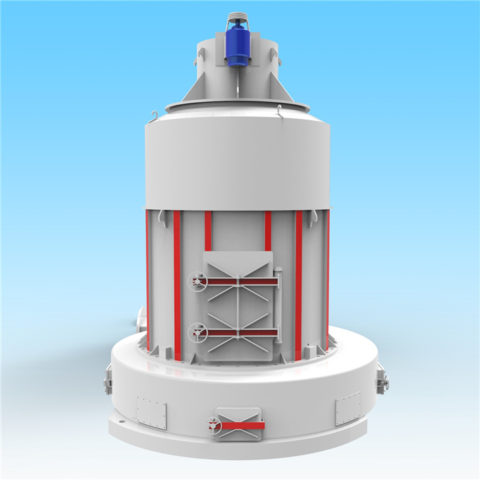
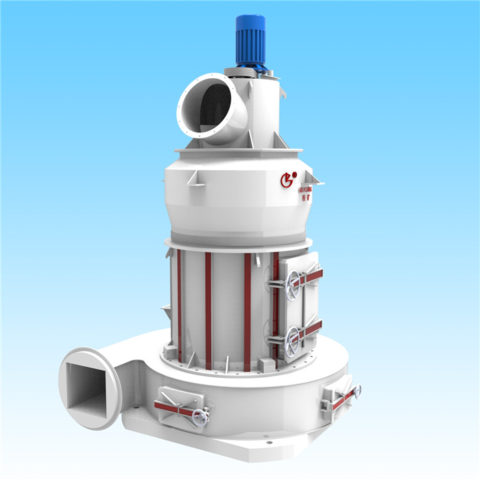
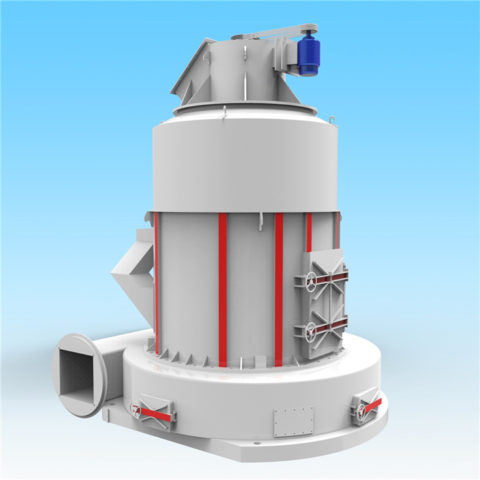
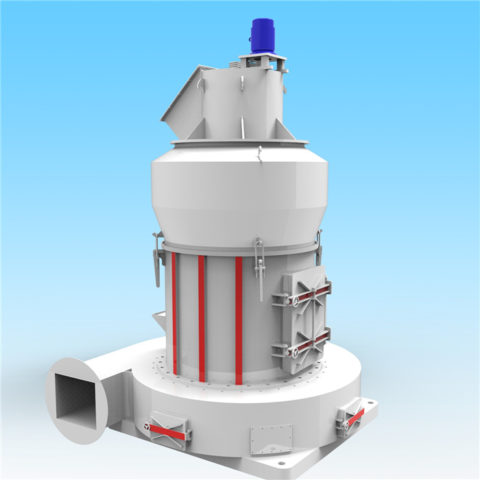
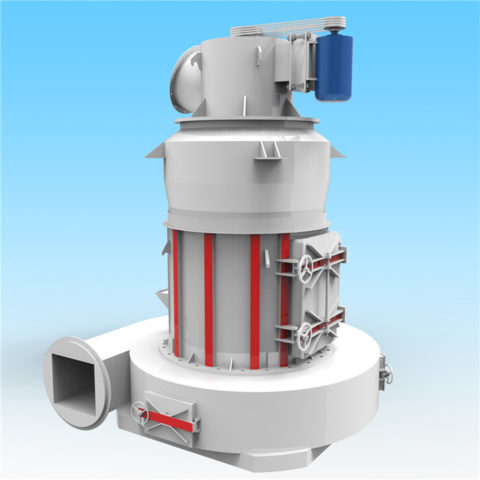
Gypsum production plants vary widely in scale and level of technology. They range from plants producing one or two tonnes per day using low-cost manual technologies, to plants of a thousand tonnes per day that are highly mechanized and capable of producing different types and grades of gypsum plaster or plaster boards.
Excavation is sometimes carried out by digging out an area of ground where the gypsum is located using open-cast techniques. The following techniques in gypsum production plant includes crushing, screening, grinding, heating. The extracted gypsum will be first crushed for size reduction, and then screened to separated the different particle sizes. The oversized material will be further grinded and then conveyed for further processing.
Gypsum ore, from quarries and underground mines, is crushed and stockpiled near a plant. As needed, the stockpiled ore is further crushed and screened to about 50mm in diameter. If the moisture content of the mined ore is greater than about 0.5 weight percent, the ore must be dried in a rotary dryer.
Ore dried in a rotary dryer is conveyed to a roller mill, where it is ground to the extent that 90 percent of it is less 100 mesh. The ground gypsum exits the mill in a gas stream and is collected in a product cyclone.