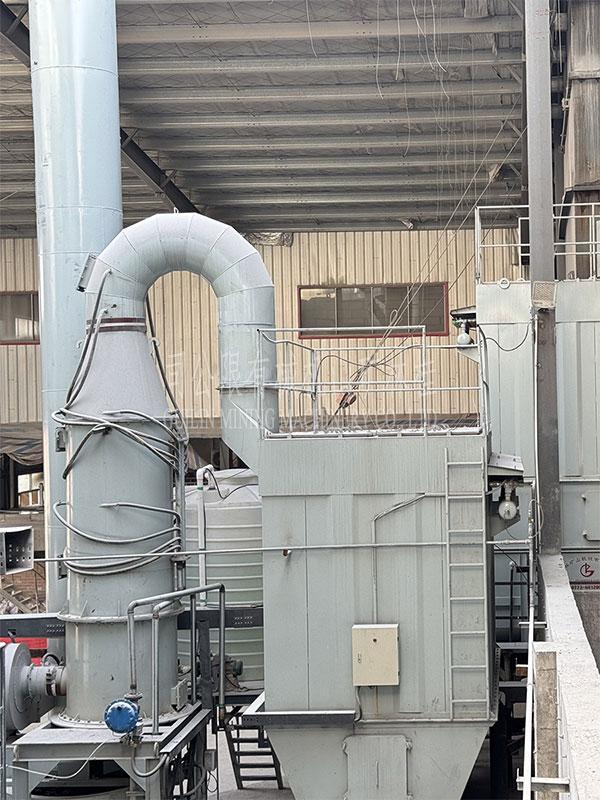
To ensure the stability and quality of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)₂) during production, the following measures can minimize moisture absorption and caking:
1. Optimize Raw Material Selection and Pretreatment
Use high-purity limestone (CaCO₃) with minimal impurities to reduce hygroscopic byproducts.
Control the calcination temperature (typically 900–1000°C) to produce reactive quicklime (CaO) with uniform particle size, which ensures complete hydration and reduces residual unreacted particles.
2. Enhance Hydration Process Control
Temperature management: Maintain hydration temperatures above 80°C to accelerate reaction kinetics and evaporate excess moisture, preventing premature caking.
Automated water ratio adjustment: Employ real-time monitoring systems to precisely control the water-to-CaO ratio, avoiding overhydration or incomplete reactions.
Multi-stage digestion: Utilize sequential hydration chambers to ensure thorough mixing and uniform particle formation, reducing localized moisture accumulation.
3. Improve Drying and Packaging Conditions
Rapid drying: Use fluidized bed dryers or rotary dryers to reduce moisture content to <1% before packaging.
Moisture-proof packaging: Seal calcium hydroxide in multi-layer laminated bags with desiccants (e.g., silica gel) to block air and humidity.
Storage environment: Store products in dry, ventilated areas (<85% humidity) at temperatures above 0°C, away from direct sunlight and acidic substances.
4. Additive Incorporation
Introduce anti-caking agents (e.g., stearic acid or silica nanoparticles) during milling to form a hydrophobic layer on particle surfaces, reducing agglomeration.
Use surfactants (e.g., sodium lauryl sulfate) to stabilize colloidal dispersions and inhibit crystallization.
5. Equipment Maintenance and Process Monitoring
Prevent blockages: Regularly clean pipelines and storage silos to remove residual moisture or hardened deposits.
Corrosion resistance: Use stainless steel or polymer-lined equipment to minimize material degradation and contamination.
Real-time sensors: Install humidity and temperature sensors in critical production zones to trigger alerts for immediate adjustments.
6. Post-Production Handling
Avoid prolonged exposure: Limit product contact with ambient air during transportation or repackaging.
Batch testing: Conduct periodic quality checks (e.g., moisture content, particle size distribution) to detect early signs of caking.
By integrating these strategies, manufacturers can effectively mitigate moisture absorption and caking, ensuring calcium hydroxide retains its chemical efficacy and flowability throughout its lifecycle.