The term “fly ash” refers to a fine powder that is a byproduct of burning pulverized coal in electric generation power plants. It is composed of particulate matter that is driven out of the combustion process with flue gases.
Fly ash is a versatile material with various uses across different industries. Its application has gained popularity due to its beneficial properties and contributions to sustainable practices.
Fly ash grinding mills are equipment used for processing fly ash, a byproduct of burning pulverized coal in power plants. The grinding mills play a key role in the mechanical activation of fly ash, turning it into a fine powder that can be used in various applications.
Grinding Process: The primary purpose of fly ash grinding mills is to break down the large particles of fly ash into smaller and finer particles. This is typically achieved through mechanical grinding processes.
Mill Types: There are various types of grinding mills used for processing fly ash. Common types include ultrafine grinding mills, Raymond mills, vertical roller mills, and ball mills. Each type has its own set of advantages and is suitable for different applications.
Ultrafine Grinding Mills: These mills are designed for very fine grinding, producing ultrafine particles. They are suitable for applications where a high degree of fineness is required.
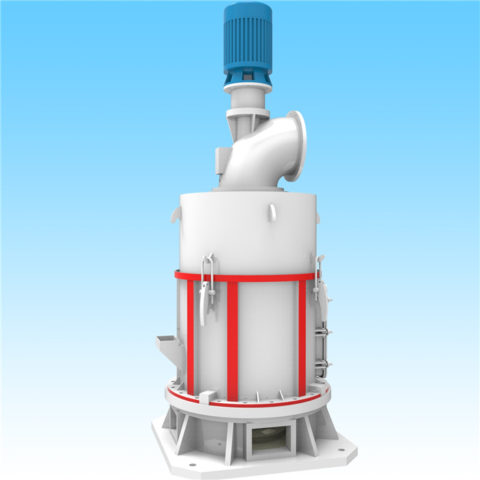
Grinding mill is a type of ultrafine grinding mill known for its high efficiency and precision in producing fine and superfine powders. It can be used for the processing of various materials, including fly ash. Here’s how the micro powder grinding mill typically works for fly ash processing:
ultrafine grinding mill for fly ash
Loading the Mill:
Fly ash is introduced into the micro powder grinding mill from a storage container or conveyor.
Grinding Mechanism:
The mill is equipped with a set of grinding rollers and a grinding ring. The rollers rotate around the central axis, and the grinding ring is fixed.
The material is fed between the grinding rollers and the grinding ring.
High-pressure springs maintain a constant pressure between the grinding rollers and the grinding ring.
The intense grinding action results in the pulverization of the fly ash particles.
Airflow and Classification:
Air is introduced into the mill to carry the ground particles upward to the classifier or collection system.
The classifier separates the finer particles from the coarser ones based on their size.
Particle Size Reduction:
The finer particles are carried by the air to the top of the mill, while the larger particles are returned for further grinding.
The grinding process achieves very fine particle sizes, often in the micron or submicron range.
Collection and Discharge:
The fine fly ash particles are collected in a cyclone collector or a bag filter, where they are separated from the air.
The collected material is then discharged from the collector.
Quality Control:
Quality control measures, such as particle size analysis and chemical composition analysis, are often conducted to ensure that the processed fly ash meets specific standards.
Utilization:
The ultrafine fly ash produced by the micro powder grinding mill is suitable for various applications, including as a supplementary cementitious material in high-performance concrete.
The fine particle size enhances reactivity and pozzolanic properties.
Raymond Mills: Raymond mills are equipped with rotating shafts with arms or impellers that impact and grind the material. They are commonly used for grinding non-metallic minerals.
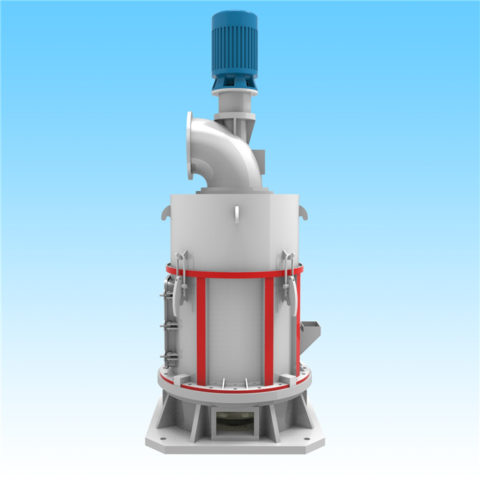
Raymond mill is another type of grinding mill commonly used for processing fly ash. Similar to ball mills, Raymond mills use rotating shafts with arms or impellers to impact and grind the fly ash particles. Here’s how a Raymond mill for fly ash typically works:
Raymond mill for fly ash
Loading the Mill:
Fly ash is fed into the Raymond mill from a storage hopper or a conveyor.
The material is introduced into the grinding chamber between the grinding roller and the grinding ring.
Grinding:
The grinding roller rotates around the central axis, and the fly ash is pressed against the grinding ring.
The material is ground by the rollers as it moves radially outward.
Airflow and Classification:
Air is introduced into the mill to carry the ground particles upward to the classifier.
The classifier separates finer particles from coarser ones based on their size.
Particle Size Reduction:
The finer particles are carried by the air to the top of the mill, while the coarser particles are returned to the grinding zone for further grinding.
The grinding action between the rollers and the grinding ring reduces the fly ash particles to the desired fineness.
Collection and Discharge:
The fine fly ash particles are carried by the air stream to a cyclone collector or a bag filter, where they are separated from the air.
The collected material is then discharged from the collector.
Quality Control:
Quality control measures, such as particle size analysis and chemical composition analysis, may be conducted to ensure that the processed fly ash meets specific standards.
Utilization:
The finely ground fly ash from the Raymond mill is often used as a supplementary cementitious material in the production of concrete.
It improves the properties of concrete, including strength, durability, and workability.
Vertical Roller Mills: Vertical roller mills use rollers to grind materials. The material is fed into the mill between the rollers and the grinding table. The rollers exert pressure on the material, and it is ground to the desired fineness.
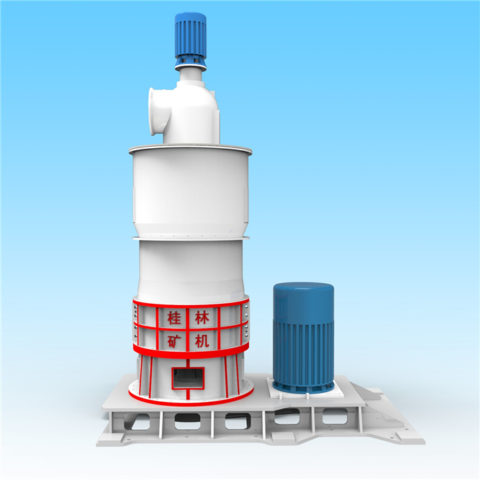
Vertical roller mills are commonly used for the grinding and processing of fly ash.The are efficient grinding mills that utilize a rotating vertical grinding table and rollers to crush and grind the fly ash particles. Here’s how a vertical roller mill for fly ash typically works:
vertical roller mill for fly ash
Loading the Mill:
Fly ash is fed into the vertical roller mill from a storage container or conveyor.
Grinding Mechanism:
The mill consists of a rotating grinding table and sets of rollers positioned around the table.
The grinding table is mounted on a central shaft, and the rollers exert pressure on the material as it passes between them and the grinding table.
The compression and grinding action between the rollers and the grinding table result in the reduction of particle size.
Airflow and Classification:
Air is introduced into the mill to carry the ground particles upward to the classifier.
The classifier separates the finer particles from coarser ones based on their size.
Particle Size Reduction:
The finer particles are carried by the air to the top of the mill, while the larger particles are returned for further grinding.
The vertical roller mill achieves the desired fineness by adjusting the pressure and speed of the rollers.
Collection and Discharge:
The fine fly ash particles are collected in a cyclone collector or a bag filter, where they are separated from the air.
The collected material is then discharged from the collector.
Quality Control:
Quality control measures, such as particle size analysis and chemical composition analysis, are often conducted to ensure that the processed fly ash meets specific standards.
Utilization:
The ground fly ash produced by the vertical roller mill is used in various applications, such as in the production of concrete as a supplementary cementitious material.
The vertical roller mill enhances the reactivity and performance of fly ash in concrete.
Ball Mills: These mills use horizontal rotating cylinders filled with the material to be ground and the grinding medium (such as steel balls). The material is ground to a fine powder as the cylinder rotates.
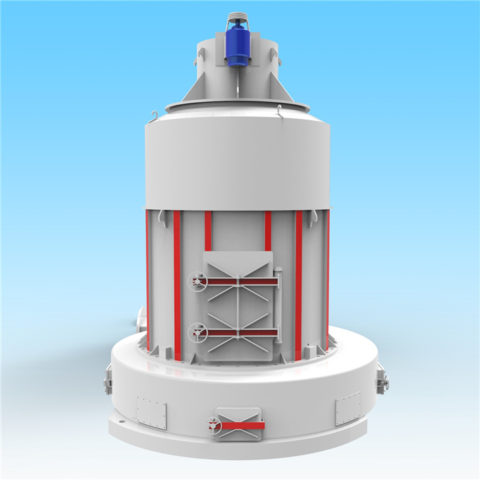
A ball mill is commonly used for grinding and processing of fly ash to achieve a fine and uniform particle size. The grinding process in a ball mill involves impact and attrition between the grinding media (balls) and the fly ash particles. Here’s how a ball mill for fly ash typically works:
ball mill
Loading the Mill:
Fly ash is loaded into the ball mill, along with grinding media (usually steel balls).
The ratio of balls to fly ash and the rotational speed of the mill are important factors affecting the grinding process.
Grinding:
As the mill rotates, the grinding media impact and crush the fly ash particles.
The impact and attrition between balls and particles result in the reduction of particle size.
Particle Size Reduction:
The grinding action in the ball mill breaks down the larger particles of fly ash into smaller and finer particles.
The goal is to achieve the desired fineness for the specific application, such as in the production of concrete.
Classifying:
In some cases, a classifier is used in conjunction with the ball mill to control the particle size distribution of the ground fly ash.
The classifier separates finer particles from coarser ones, ensuring a more uniform product.
Discharge:
The ground fly ash is discharged from the ball mill, and it may be further processed or utilized in various applications.
Quality Control:
Quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the processed fly ash meets the desired specifications.
Particle size analysis and chemical composition analysis may be conducted to verify the quality of the product.
Utilization:
The finely ground fly ash is often used as a supplementary cementitious material in the production of concrete.
It contributes to the properties of concrete, such as improved strength, durability, and workability.
Classifiers: In some cases, classifiers are used in conjunction with grinding mills to control the particle size distribution of the ground fly ash.
Application in Cement: Ground fly ash is often used as a supplementary cementitious material in the production of concrete. The grinding process enhances the reactivity of fly ash, making it more effective in improving the properties of concrete.
Environmental Benefits: Utilizing fly ash in various applications, including in construction materials, contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing the need for disposal in landfills.